 The theory of Edge Computing
The theory of Edge Computing
IoT or Internet of Things is one of the most Computing realistic parts of the cloud. There are so many devices, and with IoT evolving fast, the world will face one of the biggest challenges of processing the data acquired from these appliances. Cloud traffic is said to have increased by 3.9 zettabytes (ZB) in the year 2015 and soon, Cisco Systems predicts that this traffic is going to intensify four-fold in the year 2020 (around 14.1 ZB per year). IoT seems to be taking its rightful place in the IT industry as device-generated data is placed in a centralized storage that enables cloud computing to process it. Simultaneously, IoT’s growth rates are abominable and soon data sets will become extremely unmanageable.
This is where Edge Computing provides an answer by pushing data processing to the edge of the network rather than handling it out of a centralized data warehouse or the cloud itself, thus placing it close to the data source. This means, ideally, the processing is divided between the centralized system and the edge, thereby introducing new levels of productivity and performance especially meant for industrial companies. Edge Computing is fast being recognized as a key partner of IIoT or Industrial Internet of Things while Cloud Computing is considered as a major enabler for industrial transformation.
The concept
Conceptually, Edge Computing is not new, but there is an opportunity for industrial organizations to turn machine-based data into actionable intelligence that is closer to the source data. So, essentially IoT with its highly distributed applications works with a client – network architecture and if the devices are performing any processing, then they are in effect working with the network – edge architecture. The device requires data quickly and the basic idea is to process it at the edge so that it is received fast. In an IoT system, the reaction time is the key where data is consistently sent back to the cloud thus preventing the value from occurring. Cloud computing will still be the norm for big data analytics or for data that is not primarily time-sensitive.
On the whole, Edge computing proffers an answer to network latency that can have grave consequences for IoT. When data travels back and forth, there is a tremendous strain on the bandwidth. Besides, there is no way to transfer data back to the center as this will only delay matters, even more, thus losing critical milliseconds. Edge and Cloud work together in combination with distance and traffic to keep network speeds consistent, which would otherwise slow it down to a mere crawl. Data is gathered and processed in real-time by edge-enabled devices so that they can respond faster and perform more effectively. Edge computing along with Edge Data Centers are a versatile approach especially for network infrastructures that take advantage of the copious processing power of IoT devices.
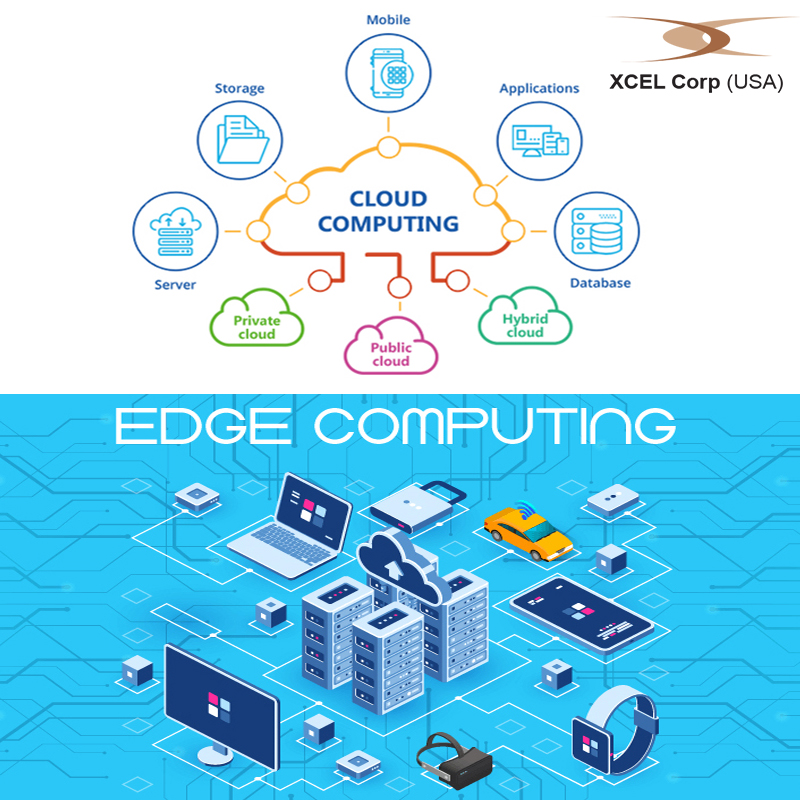
The theory of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing architecture focuses on a data center that gathers and stores data. So, devices that have to utilize this data have to connect to the cloud to source it. Generally, securing and controlling the cloud is pretty simple because it gives ample room for remote and reliable access. There are several popular public cloud services such as Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure and much more. Organizations that use traditional client-server technology and network, have tremendously benefited from these cloud provisions. Only authorized users are allowed to access information and tools stored on the centralized cloud at any time and from anywhere. But, as expressed before, data gathered from the edge of the network can be difficult to process effectively and quickly. While the cloud does have the power and capacity, speed becomes an issue. At the same time, storage and processing capacity can be expanded due to the scalable nature of a data center infrastructure.
Edge Computing Vs. Cloud Computing
Cloud computing and Edge computing are two disparate and non-interchangeable technologies. While Cloud computing processes non-time driven data, Edge computing holds the ability to process data that is time-sensitive and addresses latency effectively. Remote locations that have limited or no connectivity would prefer the Edge over Cloud computing because storage space requirements are minimal and Edge does seem to provide the perfect resolution. At the same time, while Edge computing is intelligent and comprises of specialized computing devices, for responding to specific machines in a particular way, these are not designed to perform multiple functions.
Future of the IT sector
The end of cloud computing is not here yet and speculations are unsubstantiated because the current analytical framework does not permit the adoption of Edge. Cloud computing remains a crucial part of the IT infrastructure because of the innumerable challenges encountered by IT organizations and vendors alike due to Edge’s inability to handle all applications across each environment. But a future world is evident where Edge computing will work in harmony with the cloud to deploy and manage IoT devices. This is bound to provide real-time solutions across organizations.
XCEL Corp
XCEL Corp believes that cloud computing is not a solution of choice, but imperative as IoT devices spread and become powerful. Simultaneously, we emphasize the need for effective Edge computing to leverage the potential of this technology to maximize the prospects of both the approaches and minimizing their limitations. IoT is all set to generate an astounding 1.6 ZB of data by the year 2020. Which means storage will now become a bigger concern. In the Edge computing architecture, the devices collecting the information do not have enough storage and that is why, eventually the data is deleted, which is not practical. If storage was still accomplished, even then, accessing and securing data will become a logistical nightmare.
Going forward, XCEL Corp visualizes an ideal scenario would be to combine the processing power and storage capacity of the Cloud with the data-gathering potential of the Edge. This way, companies are driven by innovation, improved services and can even keep their IoT devices running efficiently and fast.
Connect with our agents to get the best of both worlds’ solution, only from XCEL Corp. We proffer both cloud computing as well as edge computing services.